

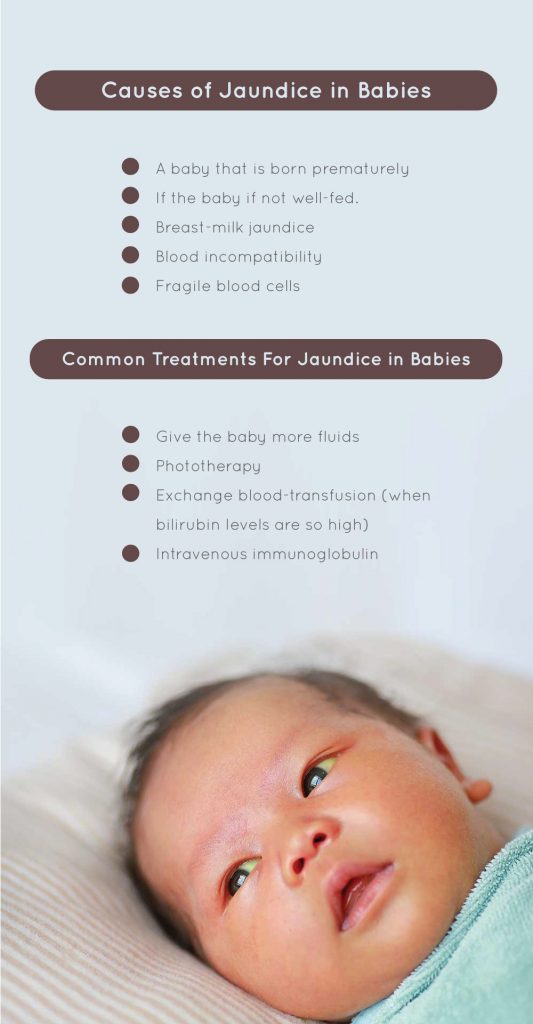
Unconjugated jaundice can be caused by neonatal sepsis, haemolysis, or endocrine/metabolic disorders. While most cases of neonatal jaundice do not have a pathological cause, many underlying diseases can present with jaundice. The breakdown of RBCs within the cephalohaematoma causes higher bilirubin levels and predisposes to jaundice.
Conjugated bilirubin is water-soluble but lipid insoluble, so it cannot cross the blood-brain barrier.Ĭonjugated bilirubin is transported to the small intestines via the biliary system and some is converted back to unconjugated bilirubin by the enzyme β-glucuronidase. Most unconjugated bilirubin circulates bound to albumin, but some circulate as ‘free’ bilirubin, which is lipid-soluble and can cross the blood-brain barrier.Īn enzyme in the liver, called UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT), converts unconjugated bilirubin to conjugated bilirubin by adding an amino acid.

3īilirubin is produced from the breakdown of red blood cells (RBCs). Understanding neonatal jaundice requires knowledge of bilirubin metabolism (Figure 1). You might also be interested in our medical flashcard collection which contains over 1000 flashcards that cover key medical topics.Īetiology Physiology of bilirubin metabolism


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
